Understanding IT Infrastructure: Stand-Alone Servers, 3-Tier Architecture, and Hyper-Converged Systems Explained Simply
When it comes to setting up the technology backbone of a business, understanding the different infrastructure models is crucial. Three common setups are stand-alone servers, 3-tier architectures, and hyper-converged infrastructures (HCI). Let’s explore these in simple terms.
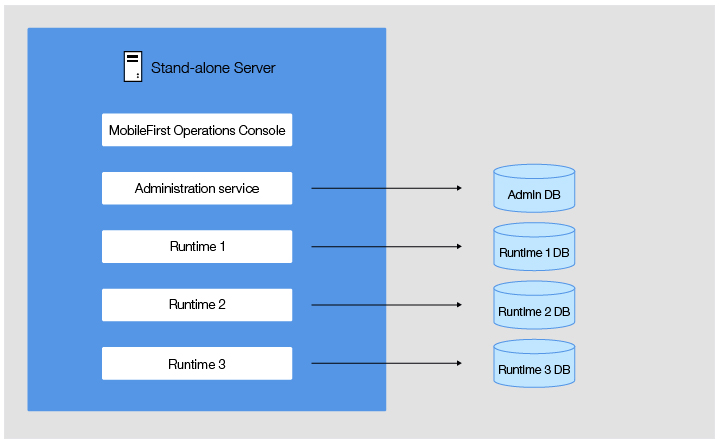
1. Stand-Alone Server
Imagine a stand-alone server as a powerful computer dedicated to handling specific tasks for a business. This server operates independently, managing its own storage and processing. It’s like having a single, robust machine running applications or storing data without relying on other systems.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to set up and manage, suitable for small businesses with straightforward needs.
- Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment compared to more complex systems.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Scalability: As your business grows, a single server might struggle to keep up with increased demands.
- Single Point of Failure: If the server encounters issues, it can disrupt business operations.
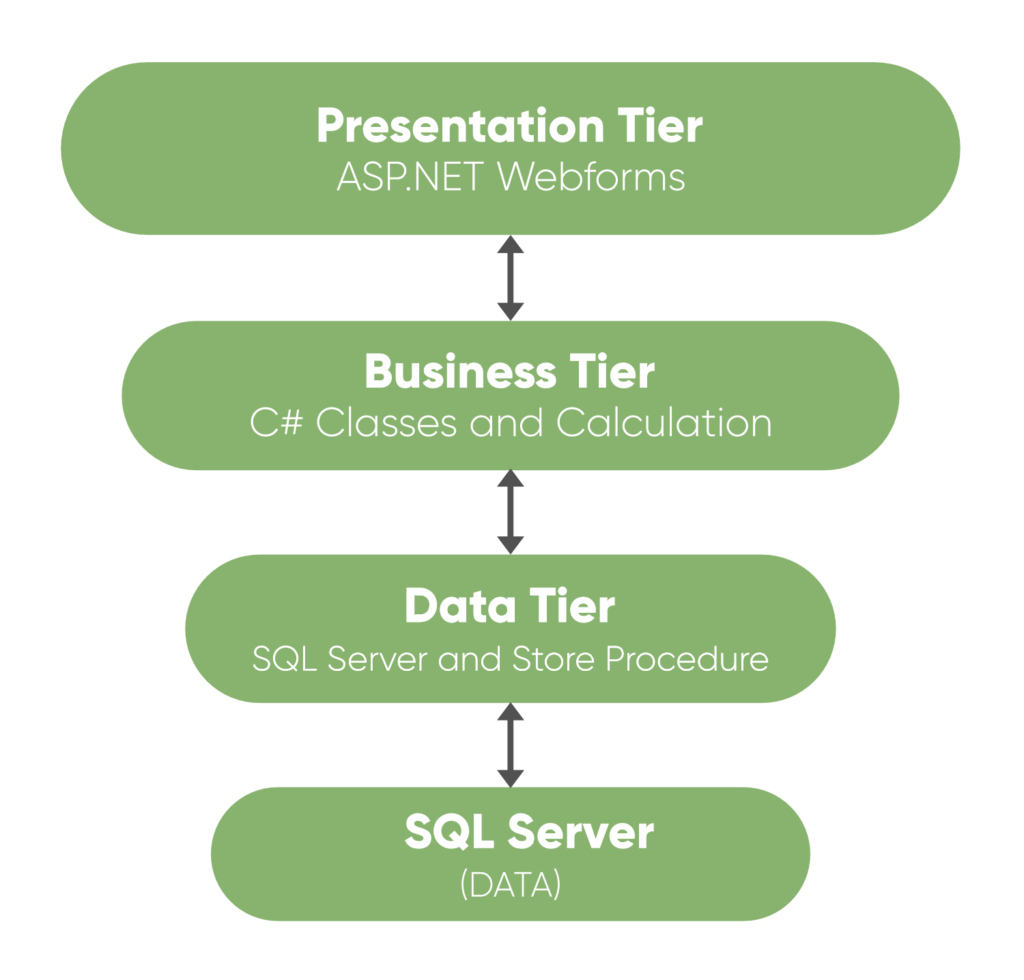
2. 3-Tier Architecture
A 3-tier architecture divides a system into three layers:
- Presentation Layer: The user interface, like the website or application you interact with.
- Application Layer: The behind-the-scenes processing that handles business logic.
- Data Layer: Where data is stored and managed.
Think of it as a restaurant:
- Waitstaff (Presentation): Takes your order.
- Kitchen (Application): Prepares your food based on the order.
- Pantry (Data): Stores the ingredients.
Advantages:
- Flexibility: Each layer can be updated or scaled independently.
- Improved Performance: Tasks are distributed, preventing any single layer from becoming a bottleneck.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: Setting up and managing multiple layers requires more effort and expertise.
- Cost: Maintaining separate systems for each layer can be more expensive.
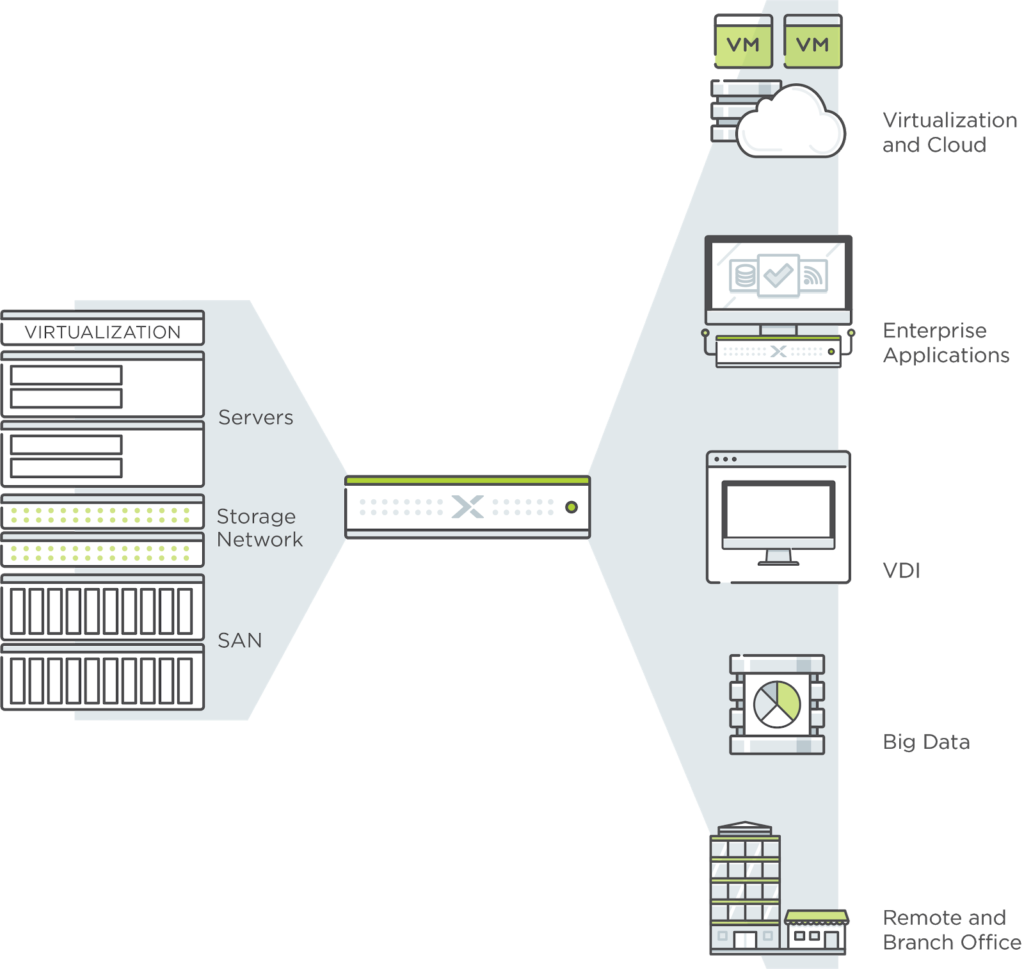
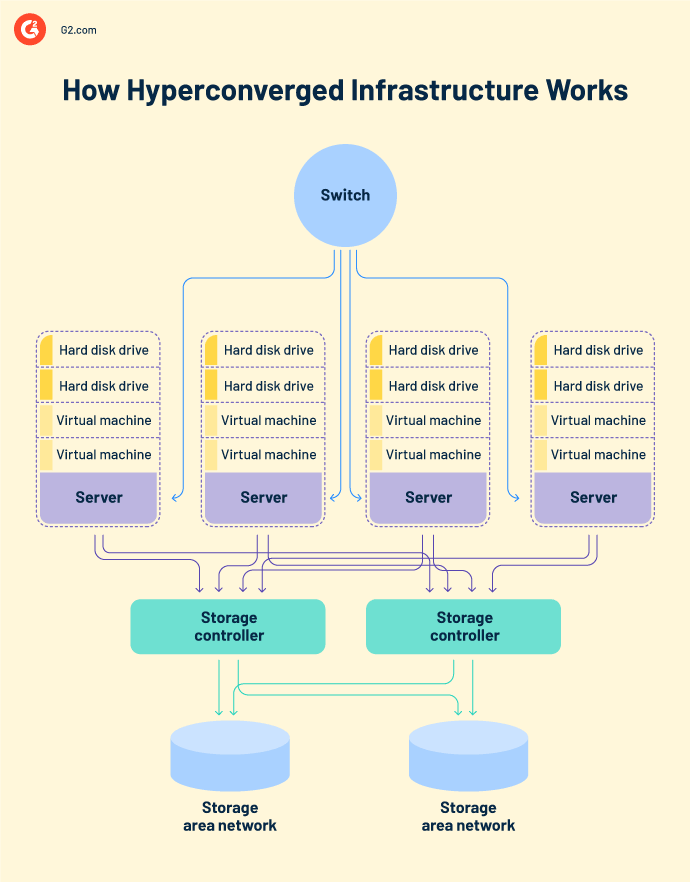
3. Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI)
HCI combines computing, storage, and networking into a single system managed through software. It’s like a multi-tool that integrates various functions into one device, simplifying management and scalability.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Unified management reduces complexity.
- Scalability: Easily add more units to expand resources as needed.
- Cost Efficiency: Combining resources can lower both hardware and operational costs.
Disadvantages:
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost can be higher due to integrated components.
- Vendor Lock-In: Relying on a single vendor for all components might limit flexibility.
Comments are closed.